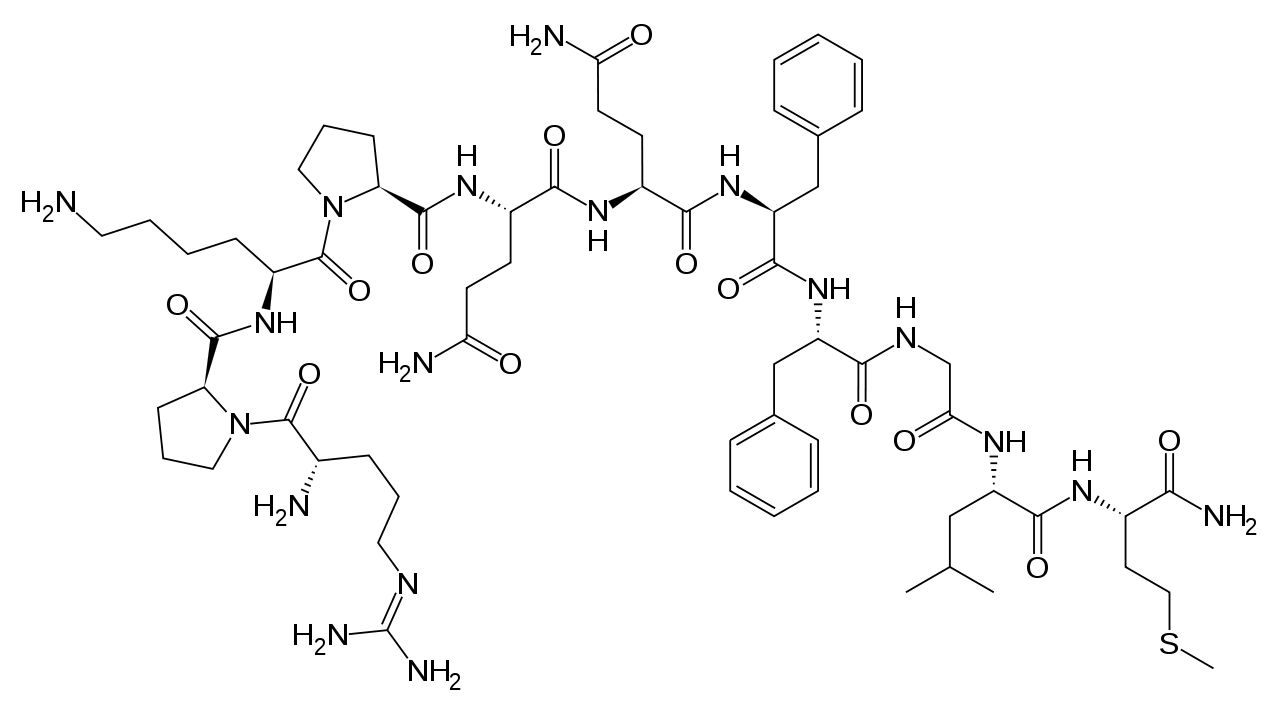
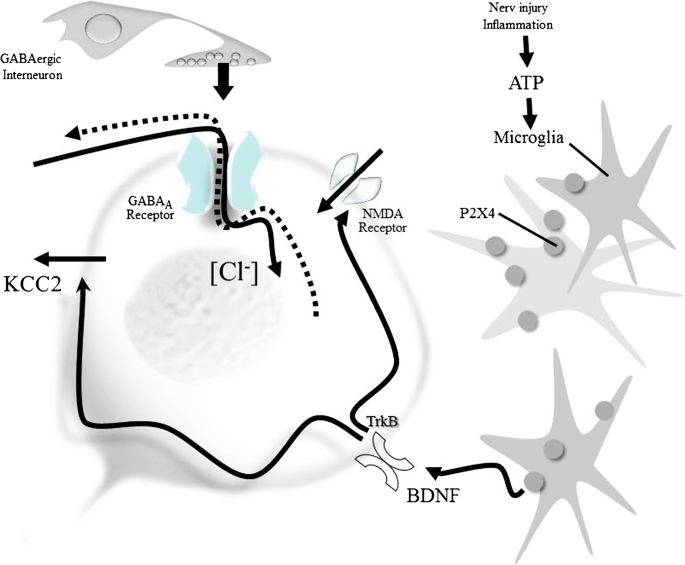
Substance P Release by Sensory Neurons Triggers Dendritic Cell Migration and Initiates the Type-2 Immune Response to Allergens - ScienceDirect

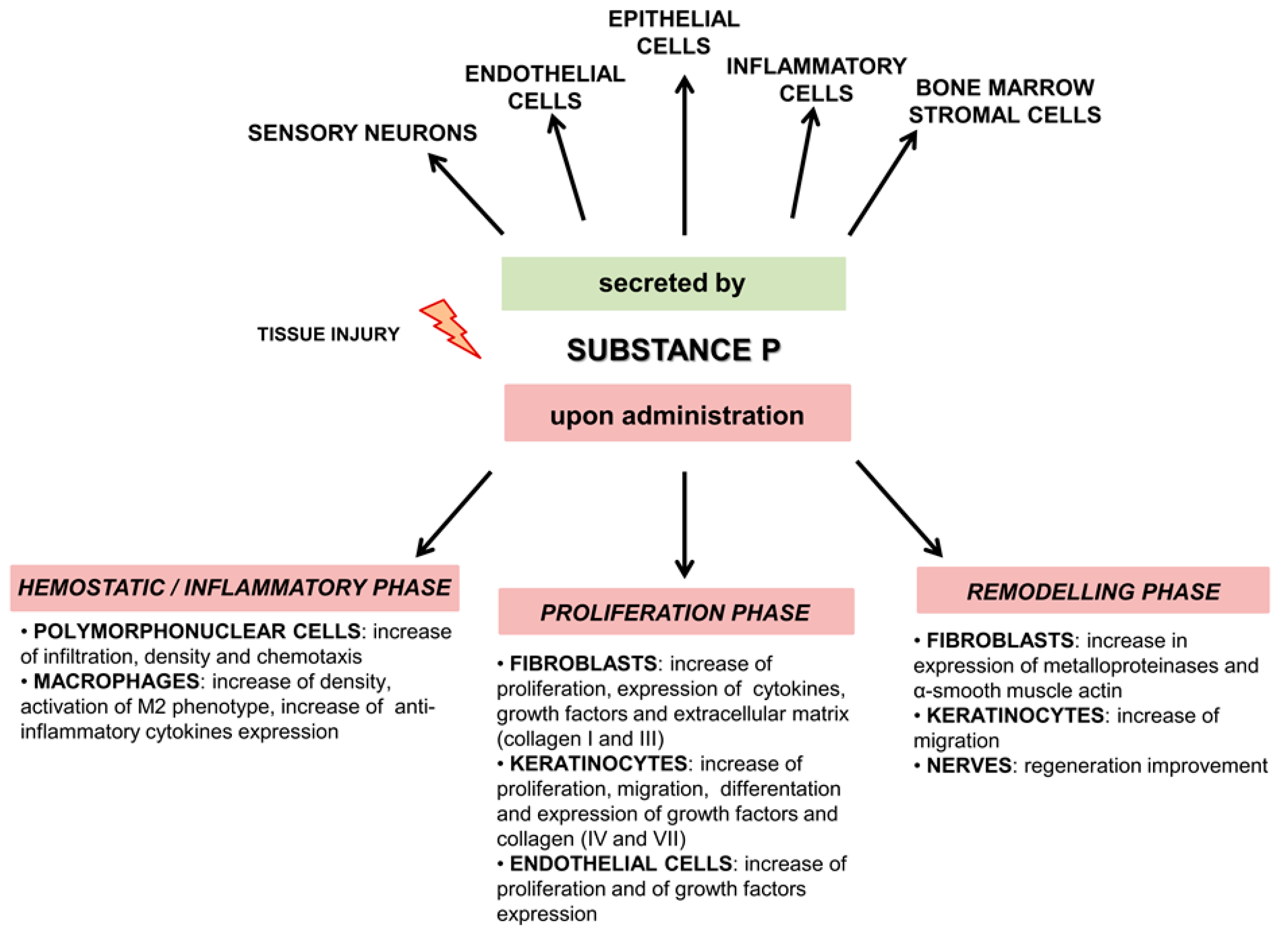
Pharmacology of Neuropeptides: Substance P, Vasoactive Intestinal Peptides, Neuropeptide Y, Calcitonin Peptides and Their Receptors | SpringerLink

Intrathecally administered substance P activated the spinal defecation center and enhanced colorectal motility in anesthetized rats | American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology

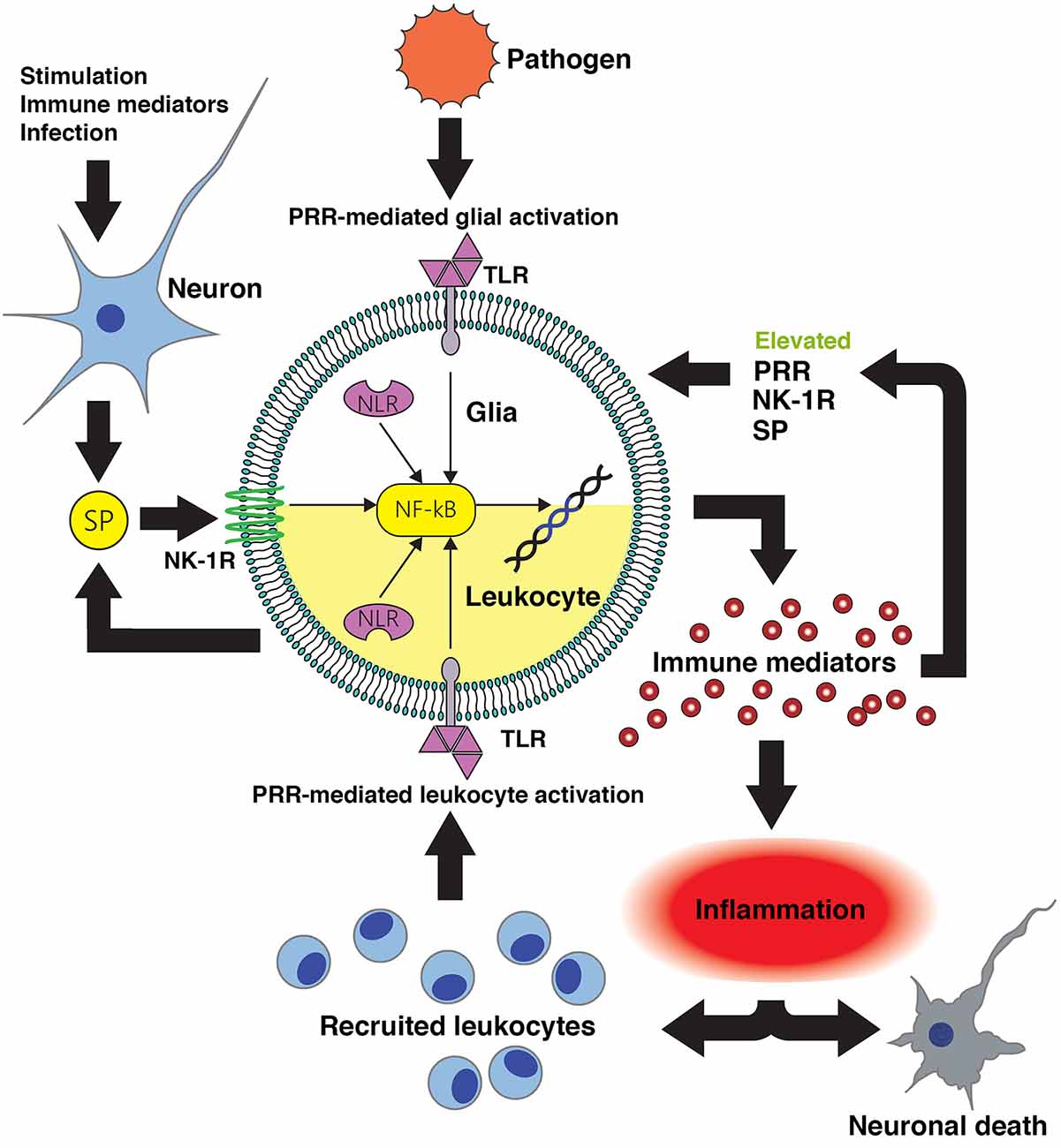
Scheme of biological functions of substance P. Once the nerve ending... | Download Scientific Diagram
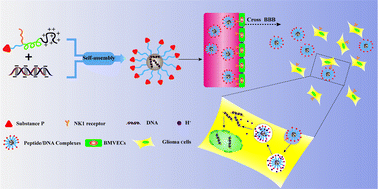
Substance P containing peptide gene delivery vectors for specifically transfecting glioma cells mediated by a neurokinin-1 receptor - Journal of Materials Chemistry B (RSC Publishing)
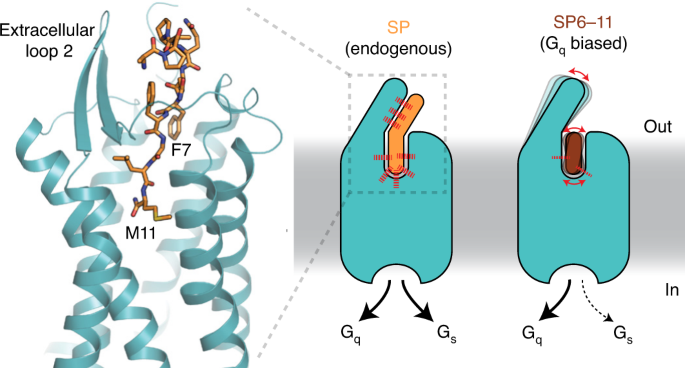
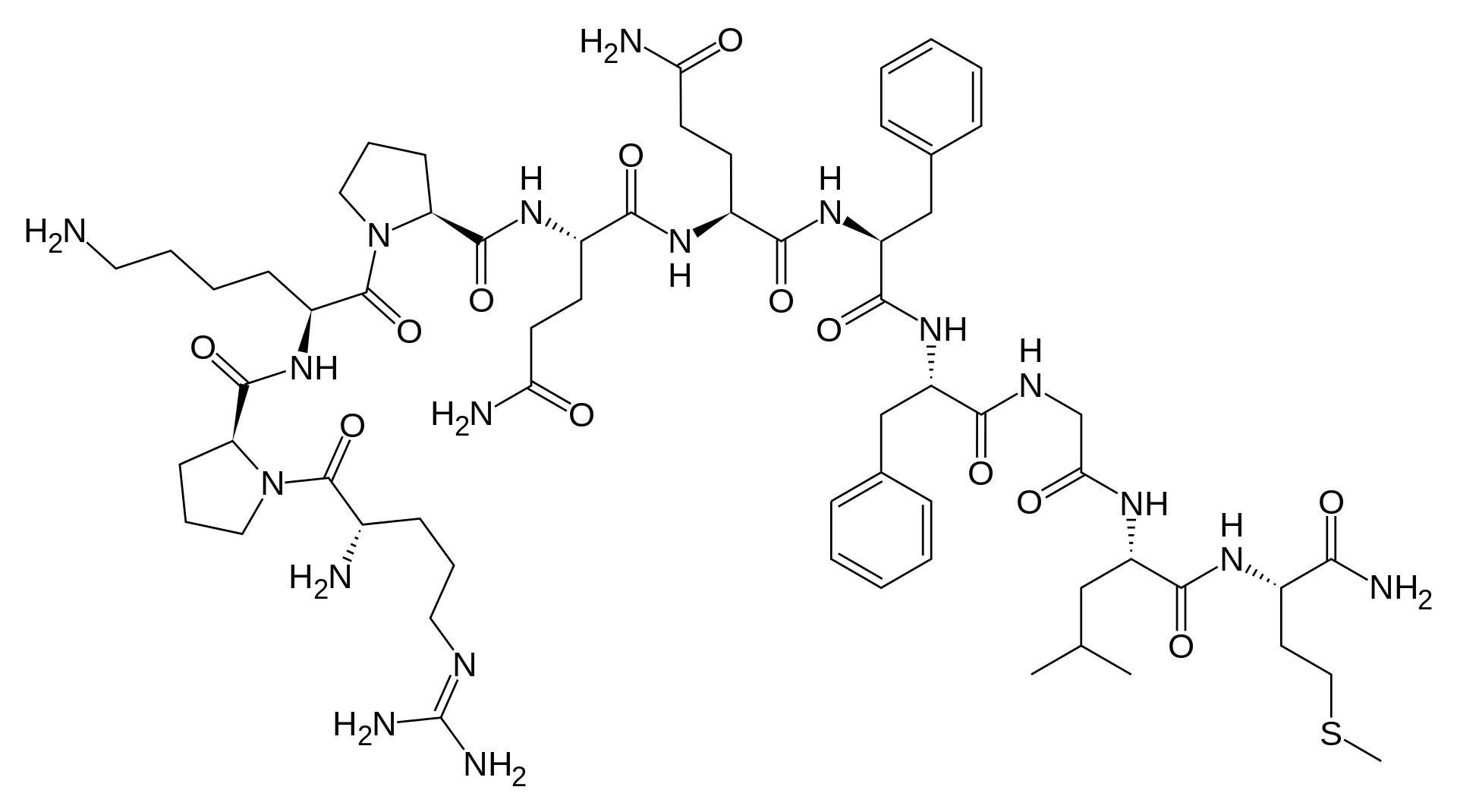
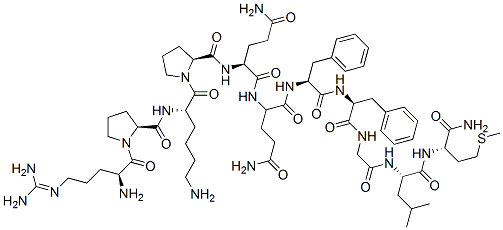
Selective G protein signaling driven by substance P–neurokinin receptor dynamics | Nature Chemical Biology